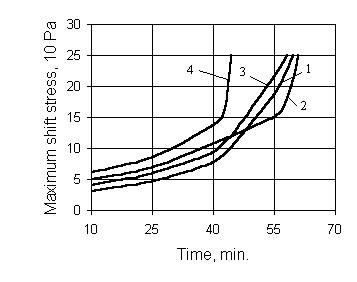
Fig. 1. Influence of FHUZh-12 concentration on maximum shift stress of a polymeric mix.
1 Ė without the additive,
2 Ė 1%,
3 Ė 3%,
4 Ė 5%.
| publiziert
in:
14. Internationale Baustofftagung (14. ibausil) 20.-23. September 2000, Weimar, Bundesrepublik Deutschland, Band 2, S. 831-836 |
Proshin A.P., Vtorov B.B.
Polymeric Mortars for Building Construction Durability Increase
One of the factors lowering the building constructions, technological tanks and equipment durability is the corrosion. More than 10% of metal is ruined due to the corrosion, that means that only in Russia, for example, irrevocable losses of steel are estimated at several million tones. The given figures donít reflect in full the real losses caused by metal construction and product ruining. More losses are connected with building construction and technological equipment damage.
At chemical factories and machine-building enterprise galvanic shops the processes of the corrosion are especially intensive. In industrial countries the losses caused by the corrosion have already reached the size compared to the expenses for main industries development.
Building constructions and technological equipment are exposed to the intensive corrosion at special enterprises. Complex reagents and not individual ones are used in technological processes at many enterprises. These technological media are extremely aggressive to many building materials.
Therefore building construction and technological tank protection in different operating conditions is an urgent economic problem.
To increase building construction durability special measures are taken in designing an industrial enterprise. Especially interesting and perspective direction is the using for anticorrosion of various polymeric materials.
In recent years some composite materials on reactoplast basis are being widely used in the world practice to protect building constructions. Such building materials as mastics, polymeric mortars and polymeric concrete on furfurane, epoxy and polyester pitch basis are widely used for these purposes.
The special literature analysis indicates that polymeric composites on furfurane, epoxy and polyester pitch basis have been investigated well enough on chemical resistance to various aggressive media, especially in mineral acids solutions such as chamois, hydrochloric and nitric acids.
However highly filled polymeric composites on the basis of listed above pitches in hydrofluoric acid solution as well as in hydrofluoric and chamois, hydrofluoric and nitric mixes havenít been investigated yet. These acid solutions are widely used for uranium production, various fluoride carbons synthesis, for chemical glass polishing and in galvanic covering production. Thatís why resistant to such media material manufacture is very important.
For building construction anticorrosion protection itís necessary to have such materials that would possess both sufficient chemical resistance to extremely aggressive media and enough adhesion to metal and concrete and would be simple for manufacturing.
For this purpose polymeric materials on epoxy pitch basis have been worked out by the authors. Various dispersion powders of FK, FM, OK marks have been used as fillers. Superficially active substances of FHUZh marks have been used to improve plastic-viscous properties of polymeric mixes. AD-20 epoxy pitch according to its reologic properties belongs to highly viscous Newton liquids which leads to some difficulty in usage of increased amount of mineral fillers.
As the tests have shown (Table 1) the composite initial temperature influences the reologic properties of a polymeric mortar.
Table 1. Components temperature influence on reologic properties of a polimeric mortar (polymer : filler = 1:6).
|
Temperature, 0 С |
Maximum shift stress, 10 Pa |
||||||
|
Hardening period, min |
|||||||
|
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
60 |
70 |
|
|
20 |
62,0 |
89,5 |
94,6 |
98,6 |
138,6 |
145,4 |
13125 |
|
30 |
51,6 |
66,8 |
87,3 |
94,4 |
131,2 |
143,5 |
25485 |
|
40 |
39,8 |
46,7 |
71,1 |
123,1 |
145,3 |
13214 |
- |
|
50 |
31,0 |
35,4 |
79,5 |
129,4 |
185,0 |
5986 |
- |
|
60 |
23,1 |
29,5 |
68,4 |
197,1 |
2418 |
- |
- |
|
70 |
15,3 |
19,6 |
51,2 |
4715,1 |
Stone-like material |
||
Before mixing components temperature increase promotes effective plasatification of polymeric mortar mixes in the first 30 minutes after making and then - acceleration of the composition hardening.
Plastification of a polymeric mortar mix has activated character and is caused first of all, by the epoxy binding reologic properties change connected with the temperature increase. Epoxy polymers are characterised by special static balls the size and quantity of which depend on both the polymeric chain configuration and their molecular and segmental mobility. When the epoxy binding temperature increases the segmental and molecular mobility considerably increases too, that raises the probability of epoxy oligomere molecules involving in the forward movement and promotes the infringement of polymer ball structure. As a result, the binding viscosity falls and the maximum shift stress of a polymeric mix is reduced. It enables to put into the composition the increased amount of mineral filler that is the cheapest component influencing many technical properties of a polymeric covering. It is possible to achieve the improvement of plastic-viscous properties of polimeric mortar mixes with the help of superficially active substances.
On Fig. 1 the influence of FHUZh-12 on maximum shift stress of polymeric mortar mix is shown.
The analysis of the received data shows that the FHUZh additives in concentration up to 3% plastify polymeric mortar mix in the initial period of hardening (up to 50 minutes). Later they act as accelerators of the mix hardening. At the increased concentration (more than 3%) the additives accelerate the process of polymeric mortar mix hardening.
|
|
Fig. 1. Influence of FHUZh-12 concentration on maximum shift stress of a polymeric mix. 1 Ė without the additive, 2 Ė 1%, 3 Ė 3%, 4 Ė 5%. |
The mechanizm of FHUZh influence on plastic-viscous properties of epoxy materials is substantially caused by the additive electro-kinetic activity, according to which they can be related to superficially active substances. When introduced in the epoxy binding the FHUZh additives at the result of physical and chemical interaction, on the partition border Ďfiller-bindingí improve the filler pitch wetting. The FHUZh additive leads to essential change of epoxy material hardening kinetics, they accelerate the process of structure forming and promote the complete hardening of the material.
The epoxy material heat isolation has shown that the FHUZh influence upon self-heating kinetics is ambiguous and depends on the filler character and the modifier molecular weight. At the FHUZh introduction into the composition huge exothermal effect is observed, the exothermal maximum is shifted to later period of the composition hardening.
The major factor determining the reliable work of protective sheeting in aggressive medium is without defect covering material integrity. One of the reasons of micro- and macro cracks occurring in polymeric materials is the shrinkage deformation in the process of hardening.
The test have proved that the kinetics of the epoxy material linear shrinkage and the absolute size are appreciably determined by the type of a filler used (Fig. 2), its dispersion and the filler amount.
Maximum linear shrinkage of materials tested is achieved during the first 7 days and later the shrinkage deformation growth gradually lowers and it practically stops after 14 days of hardening. The maximum shrinkage (0,08%) is observed in polymeric mortar with OK-mark filler.
|
|
Fig. 2. Polymeric mortar with a filler shrinkage: 1 Ė FM, 2 Ė FK, 3 Ė OK. |
The absolute shrinkage size can essentially be lowered with the help of active additives. For epoxy polymeric mortar with OK-mark filler the maximum effect of linear shrinkage decrease has been achieved with the help of a FHUZh-12 additive in the amount of 0,25% of the pitch weight. Shrinkage deformation has decreased from 0,08% for a control mix down to 0,02%. The optimum concentration of a FHUZh-4 filler makes 1% of the pitch weight. The similar effect of the shrinkage deformation reduction was observed at introduction of a FHUZh additive into polymeric mortars on the OPHPS basis. The introduction of FHUZh additives in polymeric mortars on the FM filler basis has allowed to get a shrinkless materials that are very important for building construction protective sheeting production. The shrinkage deformation decrease has also affected the polymeric mortar inner stress.
On Fig.3 a filler influence on epoxy polymeric mortar inner stress is shown. The maximum inner stress is achieved in the process of polymeric mortar with OK-mark filler hardening.
|
|
Fig. 3. A filler influence on inner stress in polymeric mortars. 1 Ė OKR, 2 - FM, 3 - OK |
Analysing the inner stress kinetic development of a given polymeric mortar one can conclude that already at early period of hardening at the result of active chemosorbtion the polimeric binding of macro molecules mobility on the border of phase partition Ďbinding-fillerí is sharply reduced. In this case the epoxy binding cooperates with the active filler surface forming chemical ties which leads to sharp system structuresation and slows down the relaxation process. As a result inner stress in the composite structure intensively increases.
In the epoxy polymeric mortar on the FK basis the filler particles surface possess expressed hydrophobic properties. It was also estimated that FM-like fillers reduce a little the exothermic peak temperature and havdening reaction heating effect.
In this case itís possible to speak about an essential polymeric mortar hardening speed decrease. This mechanism is realised during a long enough period of time Ė up to 3 hours. However, then polymeric mortar inner stresses sliarply increase that means intensive structure forming. Itís necessary to note that FM-type filler ability to form a richer spatial grid of epoxy matrix depends directly on their pH-parameter and raises with the acidity increase.
As the tests have testified (Fig. 4) the FHUZh introduction in epoxy polymeric mortar with a FM filler leads to sharp inner decrease of the material. In this case in the initial hardening period (up to 2 hours) there is no practically inner stress in the material that testifies the smooth relaxation processes as a result of structural reorganization of the system. The FHUZh epoxy oligomer modifies as a result of particles polar groups molecular blocking that results in creation on the filler surface structural elements with alternation of active and inactive centres. Due to FHUZh additive one can get more regular material structure and effective decrease of both inner stress and microdefects in the material mass and also increase of its durability.
The durability of building construction anticorrosive protection at special enterprises depends on a variety of technological factors such as the influence of hydrofluoric and chamois acid solutions and evaporations, increased temperature of the aggressive medium and mechanical ifluence. In this connection materials used for construction protection should possess a high degree of chemical inertness, low shrinkage and small inner stress and high durability.
On Fig. 4 some experimental data of epoxy polymeric mortars with various fillers acid resistance are shown. The analysis of the date have shown that the nature of the filler essentially influences epoxy polymeric mortar chemical resistance.
|
|
Fig. 4. Polymeric mortar resistance in a Ďworkingí acid mix. Filler: 1 Ė OKR, 2 Ė FK, 3 Ė FM, 4 Ė OK. |
The highest resistance in a Ďworkingí acid mix (hydrofluoric and chamois) possess polymeric mortars on OK basis. The durability of polymeric mortars on OK basis after staying in a Ďworkingí mix of acids has increased on 15-20% that can be explained by structure concentration of the material as a result of rather strong insoluble crystal forming.
In this case the decrease of epoxy binding durability caused by chemical destruction is compensated by general increase of the material density.
The polymeric mortar on OKR basis possesses, as it has been expected, the minimum resistance in the Ďworkingí acid mix. Its durability in a year of exposition has decreased on 40-45% that testifies intensive destructive processes.
Epoxy polymeric mortars on FK and FM basis posses good resistance in a Ďworkingí mix of acids that can be explained first of all by high chemical inertness of the fillers tested to hydroflouric acid solutions.